Mkdir command in Linux allows the user to create directories . This command can create multiple directories at once as well as set the permissions for the directories. In this article we will discuss how to create a single or multiple directories in Linux using mkdir command.
So, to create folder and subfolders in a single command in linux, use -p option with mkdir command. You can use absolute or relative path names on the command line when creating new directories. To createa new directory, named Reports, within the user1 directory, use the mkdir command. Try creating several different subdirectories, and then move around within this directory structure. Use both full path names and relative path names, and confirm your location with the pwd command. As 'src' directory already exists, therefore mkdir will not create new directory with same name.
But as -p option was provided, therefore it didn't gave an error. So, when we use -p option flag with mkdir command then it will only create the directory if does not exist. We will then repack that information to one string for a today date. Then we can use it to create the directory per day or we can add it to the end of the file, like some log or the output result files. We can use the value of current date in the batch files, whenever we generating new files and folders. The batch files can use special variable named DATE and which returns the current date in the local regional format.
If a shared file or folder isn't syncing, make sure it'sadded to your account. If changes to it aren't syncing, it could have been moved, deleted, or renamed by someone you're sharing it with. If you're following along with the examples in this tutorial, it would be prudent to create these files and directories within the /tmp/ directory.
/tmp/ is a temporary directory, meaning that any files and directories within it will be deleted the next time the server boots up. For more information about securing ColdFusion tags, seeConfiguring and Administering ColdFusion. Before we create a batch script and submit it to a compute node, we will do something a bit simpler. We will create a regular script file that will be run on the login node. A script is just a file that consists of unix commands that will run when you execute the script file. It is a way of gathering together a bunch of commands that you want to execute all at once.
This is to help you understand what is happening when you submit a batch script to run on a compute node. Manually creating new folders and subfolders is time-consuming if you want to organize and manage files on your Windows 10 PC. Instead, you can create multiple folders at once using the Command Prompt, PowerShell, or a batch file. By default, the cp command runs in the same directory you are working in.
However, the same file cannot exist twice in the same directory. You'll need to change the name of the target file to copy in the same location. Some users will add _old, some will add a number, and some will even change the three-letter extension (e.g., .bak instead of .txt). This guide will show you how to copy files and directories in Linux by executing commands from the command line.
Furthermore, the commands listed below detail how to create system-wide backups or filter out and copy only specific files. File permissions help to protect files and directories from unauthorized reading and writing. Often you will have files you wish to allow others to read but not change. In other cases, you may have executable files to share.
File permissions allow you to control access to your files. Before you start experimenting with files, make sure that you are in your home directory. This is a directory established for you by your system administrator when your account was created. The SunOS command line is used to manipulate files and directories. You type in the file and directory names in conjunction with SunOS commands to carry out specific operations.
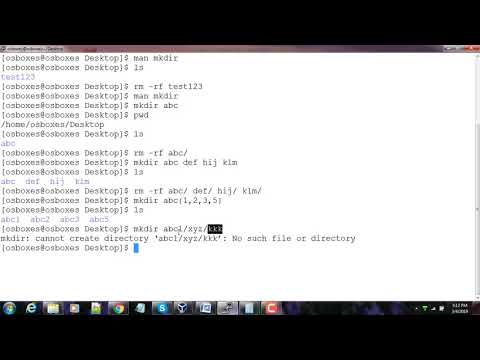
Where name_of_directory is the name of the directory one wants to create. When typed as above (i.e. normal usage), the new directory would be created within the current directory. On Unix and Windows (with Command extensions enabled, the default), multiple directories can be specified, and mkdir will try to create all of them. To list files and folders at a remote location, namemust contain a full path specified as a uniform resource locator . File templates are specifications of the default contents for new files that you create. Depending on the type of file you are creating, templates provide initial code and formatting expected in all files of that type .
You can use - or _ instead (e.g. north-pacific-gyre/ rather than north pacific gyre/). To test this out, try typing mkdir north pacific gyreand see what directory (or directories!) are made when you check with ls -F. To create a new directory named empty located inside a directory named newdir, perform the mkdir command with the -p option. You can use absolute or relative path names on the command line when creating new files. To create an empty file named space in the dir3 directory, perform the touch command. The '-c' option adds the extra information about the user and the '-U' argument creates/adds a group with the same name as the user.
The ls command also accepts some flags which are additional information that changes how files or directories are listed in your terminal. Up to this point, the discussion on permissions has only included using the chmod command to change permissions relative to their current settings. Using a different form of the chmod command, which applies numeric codes to specify permissions, you can set the permissions for a file or directory absolutely. The next nine characters indicate the permissions for the file or directory.
The nine characters consist of three groups of three, showing the permissions for the owner, the owner's group, and the world, respectively. The permissions for emptyfile are rw-r--r--, indicating that the owner can read and write this file, everyone can read it, and no one can execute it. The permissions for the directory veggies2 are rwxr-xr-x, indicating that everyone has read and execute permissions, but only the owner can write to it. I have a bash that downloads a list and if that list has data in it then a new main directory is created with several subdirectories . My question is in that list there are portion of specific file types (.vcf.gz) - identifier towards the end that have... Do you know we can create directories or files named with current date, time, month, and year from command line?
This tutorial explains how to create a directory or file with current timestamp in the name in Linux. Remember, the -p option, followed by a path of one or more directories, will cause mkdir to create any intermediate subdirectories as required. We start in the /Users/jamie/data directory, and create a new folder called recombined. The second line moves the file proteins.dat to the new folder . The third line makes a copy of the file we just moved.
The tricky part here is where the file was copied to. Means 'go up a level', so the copied file is now in /Users/jamie. Is interpreted with respect to the current working directory, not with respect to the location of the file being copied.
So, the only thing that will show using ls (in /Users/jamie/data) is the recombined folder. Using the shell to create a directory is no different than using a file explorer. If you open the current directory using your operating system's graphical file explorer, the thesis directory will appear there too. While the shell and the file explorer are two different ways of interacting with the files, the files and directories themselves are the same. Create the mydir directory, and set its permissions such that all users may read, write, and execute the contents.
ParameterInput ValueDescription-Pathstring or StringArrayPath of the items to list. The default Path is the current directory.–FilterstringFilter to apply to the Path–RecurseN/ASearch recursively through all subdirectories of the provided Path. Robert4788 pointed out something that might bite you. If "/new_folder" is a mount point for a local or remote filesystem, you might have problems if the filesystem is not mounted at the time your script runs. But that won't stop it from running--it will move your logfile to the presumably empty /new_folder.
When the filesystem is subsequently mounted to /new_folder, the previously moved files will not be visible. The "mountpoint" utility will let you know if the target directory is currently in use as a mountpoint. This is to be expected, since you're searching for files within directories that regular users typically don't have access to. However, these example commands should still work and be useful for understanding how these programs work. You can tell this by the "d" that shows up in the string of letters when you do the "ls -ltr". That's what happens when you try to cp or mv a file to a directory that doesn't exist -- a file gets created with the target name.
With the help of mkdir -p command you can create sub-directories of a directory. It will create parent directory first, if it doesn't exist. But if it already exists, then it will not print an error message and will move further to create sub-directories. The user's login directory is by convention stored in the /home directory of the workstation.
It will contain the user's personal data and the configuration files of his applications. By default, at login, the login directory is selected as the current directory. The following command will create a user 'ravi' with home directory '/var/', default shell /bin/bash and adds extra information about the user. The pwd command is included in this example to illustrate that the directory on which you perform this operation must be the current directory.
The ls -l command is shown only to illustrate the changes in permissions. When setting absolute permissions, it's not necessary to know what the permissions are currently. Path names for files work exactly like path names for directories.
The path name of a file describes that file's place within the file system hierarchy. For example, if the /home/user2 directory contains a file called report5, the path name for this file is /home/user2/report5. This shows that the file report5 is within the directory user2, which is within the directory home, which is within the root (/) directory. In early versions of Unix (4.1BSD and early versions of System V), this command had to be setuid root as the kernel did not have an mkdir syscall. Instead, it made the directory with mknod and linked in the .
The command is available in MS-DOS versions 2 and later. Digital Research DR DOS 6.0 and Datalight ROM-DOS also include an implementation of the md and mkdir commands. One of the simplest ways to backup a system is using a shell script. The archive file can then be moved or copied to another location. The archive can also be created on a remote file system such as an NFS mount.
Yoou need to have permissions to create folder for the command to work. Not having permissions to create folder would throw up 'access denied' error. Here the output of date command was passed to mkdir command and it in turn created a folder with today's timestamp.
Q. How do I create directory with current date and time? Write a shell script, which will create directories with the current date and time. Hi, After checking all the UNIX threads, I am able to come up with a solution so far. I am working on a shell script where it moves the files to a certain directory. The conditions to check are 1) Check if the file exists in the current directory. By default, the list of templates contains only predefined templates provided by PyCharm.
Some of them are internal, which means they cannot be deleted or renamed. PyCharm shows the names of internal templates in bold. The names of templates that you modified, as well as custom templates that you created manually, are shown in blue. The first two sets of commands achieve this objective. The first set uses relative paths to create the top-level directory before the subdirectories. The touch command generates a new file called my_file.txt in your current directory.
You can observe this newly generated file by typing ls at the command line prompt. My_file.txt can also be viewed in your GUI file explorer. If a file or folder should be syncing to your computer and it's not, you may be out of hard drive (or "disk") space on your computer. If this is the case, you should see an error message from Dropbox that notifies you. Learn how to check if you're out of disk space and free up space on your computer. In this tutorial, I will show you 5 usage mkdir command to create directory on a Linux and Unix like operating system.
This command changes your current directory location. By default, your Unix login session begins in your home directory. This tutorial guides you through the process of creating and submitting a batch script on one of our compute clusters.
This is a linux tutorial which uses batch scripting as an example, not a tutorial on writing batch scripts. The primary goal is not to teach you about batch scripting, but for you to become familiar with certain linux commands. There are other pages on the OSC web site that go into the details of submitting a job with a batch script. One mistake could mess up the actual folder structure, and you can always rename folders using different methods.
However, batch files can avoid that to run a simple command quickly. This article lists the most commonly used commands and tools to remove unwanted files and directories from... Once you get into any kind of programming (design, front-end, back-end, and more), you'll almost always create folders and files for your code via the command line. You'll have a huge advantage as a beginner if you're comfortable with this.